Continued COVID levels of hygiene could transform infection control and fight antibacterial resistance
Making suggestions for change, teachers from UWL’s Faculty of Biomedical Sciences and Royal Holloway’s Division of Well being Research, analyzed world information into the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in city areas—the rise of which is threatening the lifesaving position of the drugs.
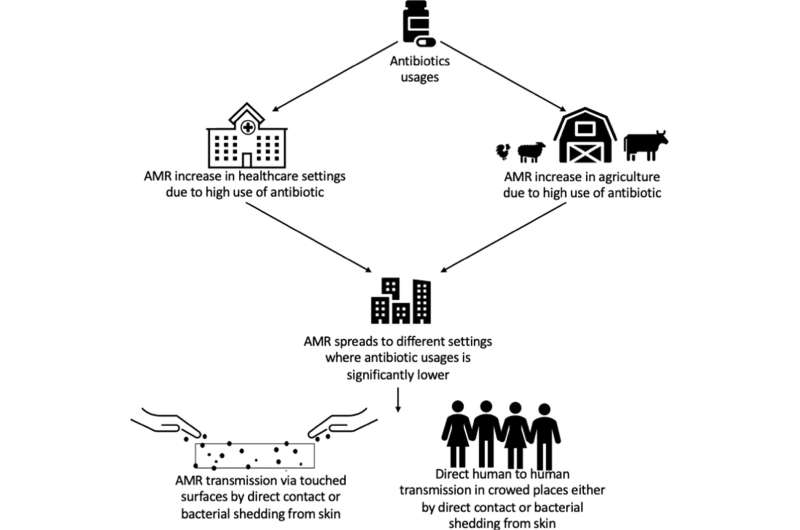
It’s estimated that with out intervention, by 2050, 10 million folks worldwide might die yearly from infections that now not reply to antibiotics. And resistant micro organism are spreading in every single place from college campuses, leisure services, and transport hubs to the handles of purchasing baskets and even in air samples—predominantly in areas of excessive human density and on regularly touched surfaces.
However regardless of the danger, little or no surveillance has been carried out into the issues exterior of wastewater and healthcare settings.
The report, “Surveillance and prevalence of antimicrobial resistant micro organism from public settings inside city constructed environments: Challenges and alternatives for hygiene and an infection management,” revealed in Setting Worldwide, seeks to establish the prevalence and surveillance of the micro organism globally, making suggestions for change and enhancements to struggle the risk.
Researchers spotlight the advantages of utilizing know-how to watch AMR unfold, designing city areas with public well being in thoughts comparable to extra hygienic transport techniques.
And that this, alongside maintaining with good hand hygiene and an infection management adopted through the COVID-19 pandemic, might drastically cut back transmission of AMR and different infectious illnesses.
Dr. Jennifer Cole, lecturer in world and planetary well being within the Division of Well being Research at Royal Holloway, mentioned: “This examine reveals the significance of not letting the higher emphasis on hygiene and an infection management we have grow to be used to throughout COVID-19 slip, as it’s simply as useful at stopping flu and the micro organism that trigger colds and sore throats too.
“Placing the science and social science collectively on this manner is a superb instance of how working throughout disciplines can enhance our understanding and assist to ship workable options. Hand-gel dispensers on buses might make an enormous distinction to the unfold of typical winter colds and flu.”
Professor Hermine Mkrtchyan, Professor of Microbiology and lead researcher on the paper, mentioned: “An infection management is extremely essential particularly throughout a pandemic, and we should have the ability to present acceptable hygiene measures to keep away from transmission whether or not its virus or micro organism.
“We all know, as seen with COVID, that transmission dangers enhance when surfaces should not sanitized recurrently and are touched a number of occasions a day, notably by folks with poor hand hygiene.
“So it’s no shock that inside overcrowded public settings, AMR micro organism are being transmitted immediately both by way of the air by shedding of pores and skin, by direct contact, or by meals.
“Lengthy-term social distancing might go a good distance in making lasting change and is extremely straightforward to undertake. Moreover, with extra strong information we are able to monitor the necessity for lasting focused hygiene interventions such because the everlasting introduction of hand sanitizing on transport and in busy areas.
“We face a severe risk to well being, and the extra we are able to be taught and adapt from exercise we have now adopted through the pandemic and with development in know-how, the extra simply we are able to result in lasting change save lives.”
Lack of entry to water, sanitation, hygiene companies in sub-Saharan Africa could have COVID impacts
Rory Cave et al, Surveillance and prevalence of antimicrobial resistant micro organism from public settings inside city constructed environments: Challenges and alternatives for hygiene and an infection management, Setting Worldwide (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106836
Quotation:
Continued COVID ranges of hygiene might rework an infection management and struggle antibacterial resistance (2021, October 11)
retrieved 11 October 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2021-10-covid-hygiene-infection-antibacterial-resistance.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.